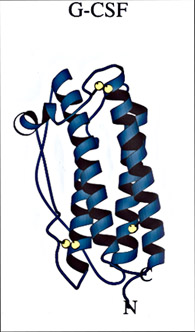
G-CSF immunity booster
1991
hormone to boost growth of white blood cells
Pure research can be expensive and time consuming. And it's often the people who apply the results of the research that make the money, while the original researchers don't.
The human body produces proteins called Colony Stimulating Factors (CSFs) that stimulate and control the growth of blood cells. CSFs were first identified and purified by scientists at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute in Melbourne after 20 years work. Their discovery sparked a worldwide race to identify and then clone the gene for human CSF by inserting it in bacteria that would then manufacture the protein. A US company, Amgen, was the first to clone the T gene for making a CSF called G-CSF.
G-CSF stimulates production of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that fights infection in our bodies. The manufactured protein was trialled in humans in 1986 and licensed for medical use in 1991.
Today, hundreds of thousands of patients are treated with genetically engineered G-CSF to boost their immune systems after chemotherapy or bone-marrow transplants.
Who Did It?
Key Organisations
Walter and Eliza Hall Institute : R&D
Amgen in USA : manufacture
Key People
Prof. Donald Metcalf, AC : team leader
R Stanley : researcher
T Burgess : researcher
Further Reading
'The colony stimulating factors --- discovery to clinical use'
D Metcalf
Proceedings of the Australian Academy of Science, April 1994.
Links
Walter and Eliza Hall Institute
of Medical Research
Amgen
Prof
Donald Metcalf
Bright
Sparcs - Donald Metcalf
Clunies
Ross Citations
CSIRO
Australia Advances
NOVA - Australian
Academy of Science
|